Latest IT Research Article
Web Application Security: A Pragratic Exposé
By Clement C. Aladi
Recommended Citation
Clement C. Aladi. 2024. Web Application Security: A Pragmatic Exposé. Digital Threats Just Accepted (February 2024). https://doi-org.ccl.idm.oclc.org/10.1145/3644394
Abstract
Many individuals, organizations, and industries rely on web applications for the daily operations of their businesses. With the increasing deployment and dependence on these applications, significant attention has been directed toward developing more accurate and secure mechanisms to safeguard them from malicious web-based attacks. The slow adoption of the latest security protocols, coupled with the utilization of inaccurate and inadequately tested security measures, has hindered the establishment of efficient and effective security measures for web apps. This paper reviews recent research and their recommendations for web security over the last four years. It identifies code injection as one of the most prevalent web-based attacks in recent times. The recommendations presented in this paper offer a practical guide, enabling individuals and security personnel across various industries and organizations to implement tested and proven security measures for web applications. Furthermore, it serves as a roadmap for security developers, aiding them in creating more accurate and quantifiable measures and mechanisms for web security.
.
Automating School Fee Transactions in Nigerian Universities and Tertiary Institutions: A Systems Engineering and System Management Approach
By Clement C. Aladi
Recommended Citation: Aladi Clement, “Automating School Fees Transactions in Nigerian Universities and Tertiary Institutions: A Systems Engineering and System Management Approach” (2019). LMU/LLS Theses and Dissertations. 943. https://digitalcommons.lmu.edu/etd/943
Abstract: This project uses system engineering and system management principles to analyze the problem of transactions in Nigerian universities and tertiary institutions. System management principles shall be used to highlight the imperfections in the transaction method currently in use, especially the disconnect between the bank and the institutions using their services. It will explore other payment systems available in the country. This project will provide a recommendation for how to implement a better payment option by automating the process of school payments by using a system with cloud-based educational software at the school bursary office and through online payment processing on the school website. The system software will enable cashiering and payment management: centralized data, automated reports, and inventory controls. It will generate automatic invoices and receipts. This system will bridge the disconnect between the bank and the school since students would not need to deposit cash directly into the school account but into their accounts and then pay with their debit cards. The system will provide debit card encryption and protection using the Secure Sockets Layer technology.
Applying the Theory of Constraints to ATM Queue Management in Nigerian Banks
Introduction
The Theory of Constraints (TOC) remains a powerful framework for improving process flows and operational efficiency. Developed by Eliyahu M. Goldratt and popularized in his seminal book The Goal, TOC focuses on identifying and managing bottlenecks — the most limiting factor in any system. Goldratt states:
“The throughput of any system is determined by its most significant constraint (bottleneck).”
Thus, to improve throughput, one must identify, manage, and eventually eliminate these constraints.
TOC is especially valuable in service operations such as banking, where customer wait times and process delays can significantly impact satisfaction and efficiency. Goldratt outlines a five-step process for applying TOC:
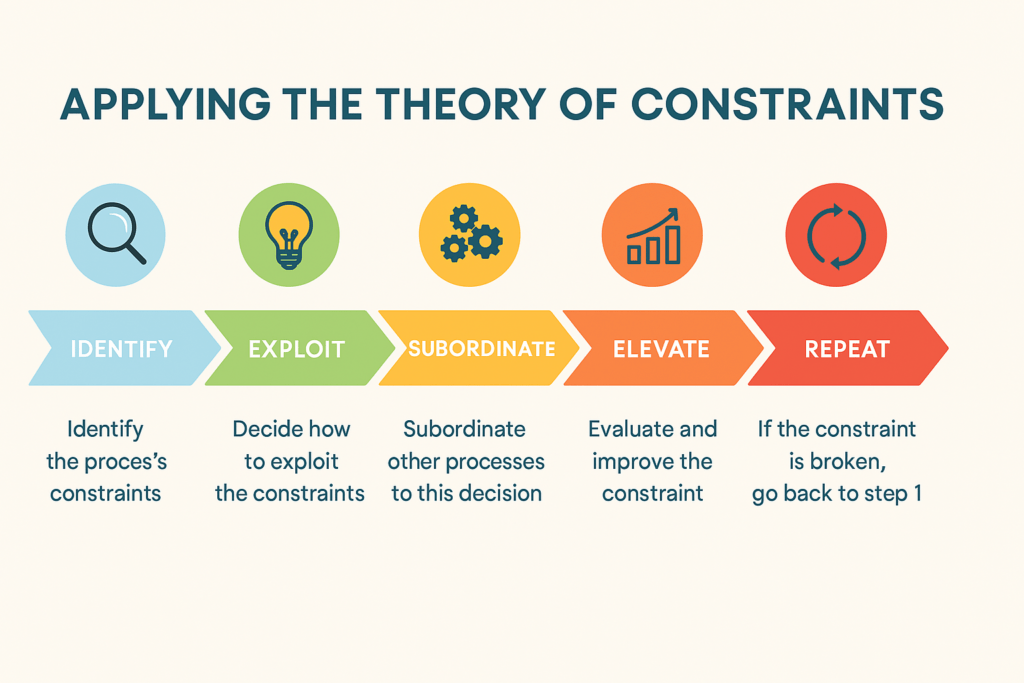
- Identify the system’s constraint(s)
- Decide how to exploit the constraint(s)
- Subordinate everything else to the above decision
- Elevate the constraint(s)
- If a constraint is broken, return to Step 1 (continuous improvement)
Problem Statement
Long queues at ATMs in Nigeria remain a persistent issue, often requiring customers to wait more than 30 minutes for a simple transaction — a sharp contrast to average withdrawal times in the U.S. (47–60 seconds). During a recent visit, I observed various inefficiencies at play, many of which are avoidable.
These queues waste valuable time, affect customer satisfaction, and reduce the overall effectiveness of banking services. By applying TOC principles, we can optimize the ATM experience and reduce unnecessary delays.
Goal
To decongest ATM queues and improve the efficiency of ATM transactions, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing operational waste.
Constraints Identified
The major constraints contributing to long ATM queues include:
- Customer-related inefficiencies:
- Customers retrieve transaction info from phones while at the ATM
- Indecisiveness during PIN setup or card activation
- Elderly or inexperienced users requiring assistance
- Use of damaged or unreadable cards
- System-related inefficiencies:
- Unstable network connectivity or poor internet bandwidth
- Machine downtime due to lack of preventive maintenance
These constraints slow down throughput and negatively affect other banking services, as resources are tied up managing ATM congestion.
TOC Application
1. Exploit the Constraints
Maximize efficiency within the current limitations:
- Customer re-orientation through educational campaigns via email, SMS, bank apps, and ATM screens
- Encourage customers to prepare transaction details before arriving
- Offer in-bank assistance to reduce time spent by inexperienced users
2. Subordinate to the Constraint
Align all other processes to support the management of the bottleneck:
- Customer service staff should ensure that best ATM practices are followed
- Direct non-withdrawal transactions (e.g., transfers, bill payments) to alternate platforms
- Banks should encourage digital banking through incentives or guided onboarding
3. Elevate the Constraint
Implement initiatives to eliminate or reduce the impact of constraints:
- Deploy dedicated e-service ATMs for tasks like transfers, airtime purchases, and PIN resets
- Introduce priority access lanes for elderly or disabled customers
- Optimize queue management using single-line systems for fair, efficient flow
- Configure machines to support bulk withdrawals (pre-set denominations) to reduce transaction time
- Train customers to avoid:
- Counting cash at the machine
- Checking balances after withdrawal
- Inserting/removing cards multiple times per session
4. Repeat the Process
Continue observing, evaluating, and improving ATM operations through feedback loops, data analysis, and pilot programs for new queue solutions.
Enterprise-Level Initiatives
- Dedicated Self-Service Zones
- Install ATM clusters inside banks or secure outdoor areas for non-cash services, thereby separating use cases and reducing congestion.
- System Infrastructure Enhancements
- Invest in high-bandwidth internet to improve ATM network reliability
- Schedule preventive maintenance to reduce unexpected machine downtimes
- Upgrade machines to ensure they can handle modern banking needs with minimal errors
Conclusion
Applying the Theory of Constraints to ATM queue management offers a structured approach to identifying bottlenecks and strategically eliminating them. With thoughtful implementation of both customer education and system-level improvements, Nigerian banks can significantly reduce ATM congestion, streamline operations, and enhance the customer experience.
LEAN THINKING
Have you heard of Lean Thinking? If you haven’t, let me quickly say it is a process of minimizing waste to increase productivity in manufacturing and in every other activity that is accomplished through various steps. Lean thinking has five principles, which include: Identifying value, mapping the value stream, creating flow, establishing pull, and seeking perfection. There is always a constraint in every system that affects the overall productivity of the system; identify those constraints(bottleneck), exploit, elevate it, and keep on improving the process while being watchful for potential bottlenecks. When you think lean, there won’t be room for waste, hence, resources will be well managed and productivity maximized. The slides posted below, describe the application of lean principles to school fees transaction. For further tutoring on Lean thinking, do well to contact me here to schedule an online session. Before then, I would recommend you read this masterpiece called THE GOAL by Eliyahu M. Goldratt and Jeff Cox.
Visual Stream Mapping
Value stream map for making pizza: •http://jensen.sdsmt.edu/IENG451/Materials/IENG%20451%20Assignment%2001.pdf •
Building process: •http://www.leansimulations.org/2011/09/value-stream-map-examples.html
QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Download to read our Latest Research

Download

Great innovative move
Thanks my most revered brother. I am following in your footsteps.